The effects of foot alignment and its influence on lower leg pain and posture
The question often been raised “Is my low back pain due to disc problem?” well it need not be all time. Often the back pain, hip or knee pain could also be more influenced due to undiagnosed or ignorance of foot-related pain and problems. Studies have implicated foot posture and foot function as risk factors for lower extremity pain. However, foot problems alone cannot be contributed for all problems related to back, knee, or hips. When your foot contacts the ground, it sends stresses up your leg and into your back, hip & pelvis and for this reason, poor alignment can cause strain and pain in any of these areas (1)
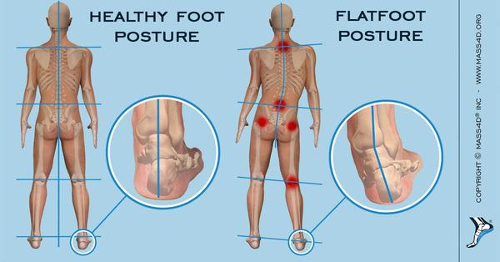
Changes in alignment of your leg must always be considered when you suffer low back pain from standing or walking and particularly is important in sports people or those with prolong standing job or with ongoing foot problems. The foot arches are mainly of two types: The medial, lateral and transverse arch.
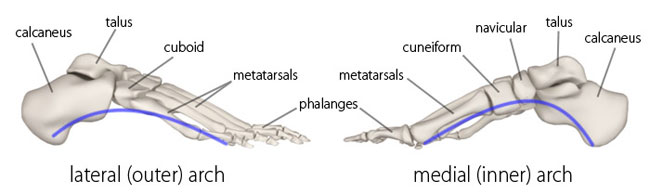
Now, usually these arches of foot are important and required to provide functional stability or balance and support to foot especially with weight bearing activities, like e.g.; standing, walking, running and related activities of daily living. The human foot is composed of the arch structure, which is characteristic in every person and deforms with aging. The arches are considered to play functionally significant roles by supporting body weight and reducing the impact of the body during running and walking (2)
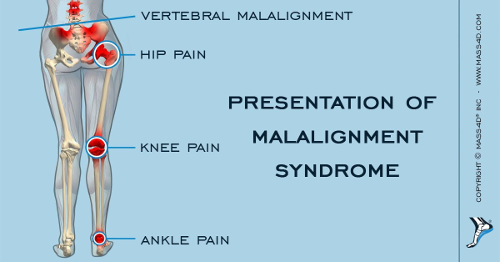
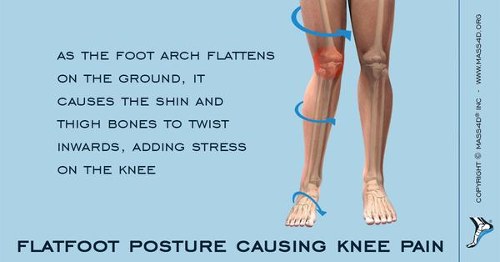
As per the image above, it represents the malalignment of foot which results in stress/strain on the chain of segments such as knee, hip, and the pelvis. From the image, we can also make out the significant disturbed malalignment of the pelvis, especially in standing owing to which back pain is an obvious outcome due to foot disorder. As in image represented above also shows impact of flat foot on knee, and how a bad foot could lead to possible undiagnosed not just back pain, but also knee pain due to foot problems.
There are various ailments of foot which alters posture especially with standing; especially in population who works with prolong standing, like teachers/professor, or in sports related activities as in athletes.
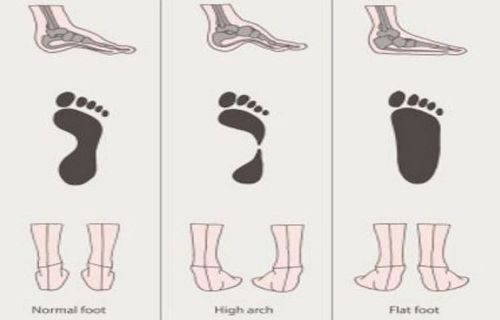
The arches of foot are mainly two; medial and lateral arch, which are meant to provide not just support , but stability to a person during the weight on leg or foot in standing, walking or running activities. As shown below are three form are arch which consist of normal, high arch (called as “pes cavus” ), flat foot (called as pes planus”). There are various other foot deformities which can cause the foot disorders, but as in regular clinical presentation these were most common source of problem in regular patients which are most likely due to musculoskeletal imbalance or lack of muscle control.
As described earlier flat foot is the most common clinical condition of many foot problems among people. Flat foot has been associated to family history, the use of footwear in infancy, obesity and urban residence and it has also been associated with age , gender and foot length (3). Studies have also shown as aging progress flat foot can dominant and could lead to foot/posture instability, bad posture and eventually risk of fall gets higher on the note (4). It is also seen, many patients with arthritis of knee have significant flat foot or foot related disorder which predispose to early age arthritic changes on the weight bearing joints like knee(5). There is other segment of foot disorder which is Pes cavus, which is high arch foot. With this kind of foot arch will place too much weight and stress on the ball and heel of the foot while standing and/or walking. These kinds of arch are typically not very common when compared to flat foot. This foot usually seen with deformity of foot followed by any disease of joint or due to bone malformation, e.g., club foot in infants(6).
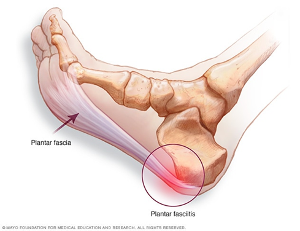
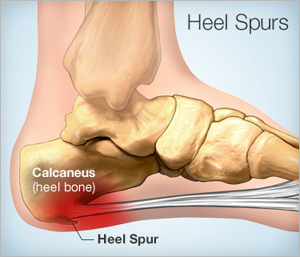
The most common outcome of flat foot is plantarfasciitis. It is a very common foot problem associated with flat foot people. Plantarfasciitis is also called as plantar heel pain. The main cause for this pain is due to flat foot, tight plantar fascia (it’s a structure that acts as protecting cover to sole of foot and prevents direct impact of forces on sole of foot), tight tendon of Achilles, extra bony growth( heel spur), obesity, work-related prolong standing.
There are different treatment approaches to relieve flat foot or any other foot related problems. A careful history, observation, and proper assessment of a health practioner could resolve this problem at earliest. Various treatments are available in physiotherapy to correct the foot arch issues and also to relieve painful foot. Some of the basic PT intervention are use of pain-relieving modalities like UST (ultrasound therapy), IFT (interferential therapy, MHT (moist heat). The pain-relieving modalities are definitely the first call of treatment as they help to reduce pain, swelling or inflammation of foot, or any discomfort across foot in acute phase (pain of initial 1 to 10 days) condition. The next phase of pain called sub-acute (varies from 2-3 weeks), exercise should be initiated. These exercises comprise of stretching the tight structures in and around foot, strengthening knee and ankle, proprioception and balance exercise to enhance ankle stability. The last phase being chronic ( > 3 weeks), requires more detailed evaluation and should be considered and is considered as a rehabilitation of ankle and foot. The other modified and advance physiotherapy includes dry needling, IASTM (instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization), Theraband exercise, wobble board exercise (to improve balance and coordination of foot). Last but, not the least the most corrective method of foot bad position could be through use of insole. Various insoles are available, but to pick the right insole need a proper evaluation and assessment of the foot which will determine the type of insole required, necessary, and useful to correct the foot pain and problems.
The UST/IFT which as earlier mentioned helps to reduce inflammation in and around plantar fascia and related structure, thus relieving pain. They are very useful in initial presentation of pain. Also due to local increase in blood flow, the healing eventually takes place and thus decreases pain (7).
Dry needling is another advance form of treatment for foot pain. The dry needling could be used if any muscle is main source of foot pain. Dry needling is mainly done if the source of pain is through a trigger point on muscle. A trigger point is a hyperirritable spot, a palpable nodule in the taut bands of the skeletal muscles' fascia (8). The source of pain is a muscle trigger point as mentioned than dry needling would be very useful and the foot pain which is more of referred source could be treated well.
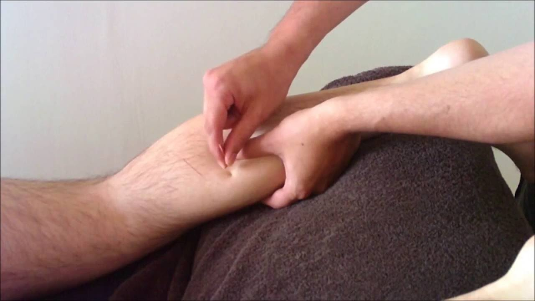
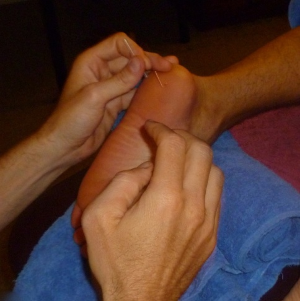
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilisation or Simply IASTM is a new range of tool which enables clinicians to efficiently locate and treat individuals diagnosed with soft tissue dysfunction (9). Studies have also showed clinical benefits of IASTM showing improvements in range of motion, strength and pain perception following treatment (10). IASTM improves the extensibility of soft tissues by treating their restrictions and when heat is generated from friction by the instrument, the viscosity of the tissue decreases, making it softer. Physiologically, a decrease in the viscosity of tissue improves joint movement (11).
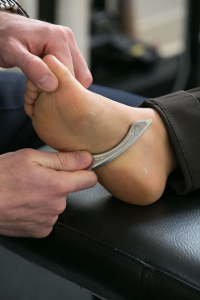
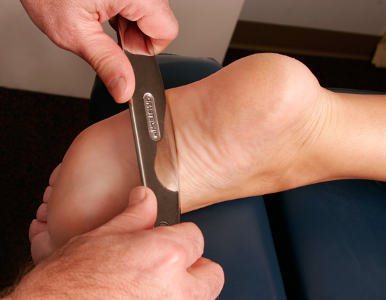
Beside these treatments, the exercises to strengthen the ankle/foot and ankle/foot balance exercise hold the most important segment of foot pain. Studies have shown foot strengthening exercise helps to increase dynamic stability and maintenance of good arch for support (12). Studies have also shown that frequent and short duration of foot strengthening exercise help to maintain a good movement of foot, balance, and posture overall and helps distribute weight on foot in uniform pattern (13).
One of the most frequent and regular use to correct foot pain and issues are use of insoles. These insoles are of varied types. Mainly divided in 3 forms:
1. Over the counter shoe inserts: The first category is over-the-counter or after-market shoe inserts. These mean exactly what their name implies. You get them after you buy your shoes. They are not prescription, and you don't need to go to a doctor or podiatrist (foot specialist) to purchase them.
2. Partial Shoe Inserts: These inserts partial covers the involved areas only. Few examples includes; heel cups, heel lifts, metatarsal pads, and 2/3 shoe inserts.

3. Full-length insole: They cover the entire sole of foot and give complete support to foot. Few examples are: Heat moldable insole, cushioned insole, and Arch-supporting insole.

We here in our Spectrum physio department, provides insole only after a proper assessment and we provide insole thereafter, later we prescribe a customized shoe insole based on patient’s need. The foot insoles we undertake are from Shape-Crunch. You may take a better look on their products as well through their website; https://shapecrunch.com
Last but, not the least the foot pain could be disabling if not treated on a right time, as it leads to more sedentary lifestyle due to less activity owing to pain. Hence, care to be taken to avoid ignorance of foot pain. A regular, periodic check of type of footwear we use in our daily living is must. Further maintaining body weight, constant change of footwear, regular exercise can also help to eliminate foot pain and foot-related problems on a long term.
References:
1. Associations of Foot Posture and Function to Lower Extremity Pain: The Framingham Foot Study. JL Riskowski,1,2 AB Dufour,1,3 TJ Hagedorn,1 Howard Hillstrom,4 VA Casey,1 and MT Hannan1,2.
2. Effects of Foot Arch Structure on Postural Stability. Emi Anzai*, Kanako Nakajima, Yumi Iwakami, Mitsuru Sato, Shuichi Ino, Toru Ifukube, Kazuhiko Yamashita and Yuji Ohta.
3. Flat Foot in a Random Population and its Impact on Quality of Life and Functionality. Salvador Pita-Fernandez,corresponding author1 Cristina Gonzalez-Martin,2 Francisco Alonso-Tajes,3 Teresa Seoane-Pillado,4 Sonia Pertega-Diaz,5 Sergio Perez-Garcia,6 Rocio Seijo-Bestilleiro,7 and Vanesa Balboa-Barreiro8.
4. The effect of flat and textured insoles on the balance of primary care elderly people: a randomized controlled clinical trial.de Morais Barbosa C1, Bértolo MB2, Gaino JZ2, Davitt M3, Sachetto Z2, de Paiva Magalhães E3.
5. Association of bilateral flat feet with knee pain and disability in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study.Iijima H1,2,3, Ohi H4,5, Isho T1,6, Aoyama T1, Fukutani N1, Kaneda E7, Ohi K4,5, Abe K4, Kuroki H1, Matsuda S8.
6. Foot health facts, Foot & Ankle Conditions » Cavus Foot (High-Arched Foot).
7. Comparison of Effects of Interferential Therapy (IFT) And Combination Therapy (IFT+Ultrasound Therapy) on Pain, Range of Motion and Function in Patients With Osteoarthritis of Knee: A Hypothesis.Vol 3 | Issue 2 | May - Aug 2015 | page:3-7 | Archana Bodhale, Nilima Bedekar.
8. Simons DG, Travell JG, Simons LS. Travell & Simons' myofascial pain and dysfunction: upper half of body. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999.[1][2].
9. Fowler S, Wilson JK, Sevier TL.Innovative approach for the treatment of cumulative trauma disorders.Work 2000;15:9-14.
10. Melham TJ, Sevier TL, Malnofski MJ, Wilson JK, Helfst RH Jr.Chronic ankle pain and fibrosis successfully treated with a new noninvasive augmented soft tissue mobilization technique (ASTM): a case report.Med Sci Sports Exerc.1998 Jun;30(6):801-804.
11. Therapeutic effectiveness of instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization for soft tissue injury: mechanisms and practical application. Jooyoung Kim,1 Dong Jun Sung,2 and Joohyung Lee1.
12. The Effect of Foot Strengthening Exercise on Dynamic Function of the Medial Longitudinal Arch in Runners: A Preliminary Report. Jarom Bridges.
13. The Influence of Plantar Short Foot Muscle Exercises on Foot Posture and Fundamental Movement Patterns in Long-Distance Runners, a Non-Randomized, Non-Blinded Clinical Trial. Iwona Sulowska,1 Łukasz Oleksy,1,2 Anna Mika,1,* Dorota Bylina,3 and Jarosław Sołtan.