Impact of flat foot on hip and knee pain
Impact of flat foot on hip and knee pain
By
Dr. Jaishree & Dr. Sumaiya
Dr. Jaishree & Dr. Sumaiya
If you have flat feet, it can also lead to poor foot posture or ankle twisting, causing an imbalance in your back, hip, and knee, resulting in pain.Flat feet are also called hyperpronated feet because it also causes the feet to roll inward when you walk or run.
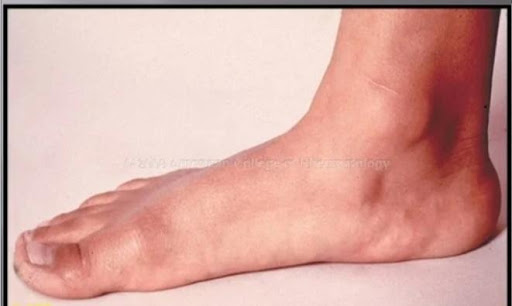
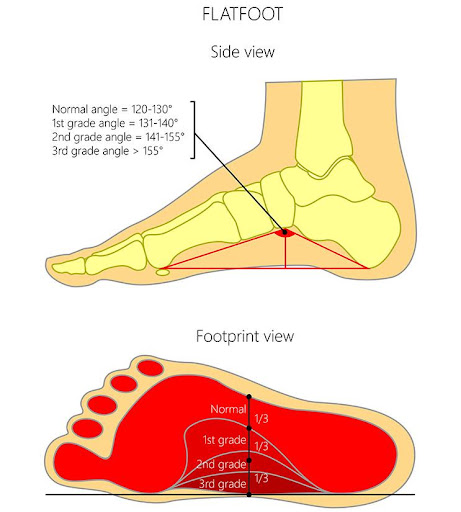
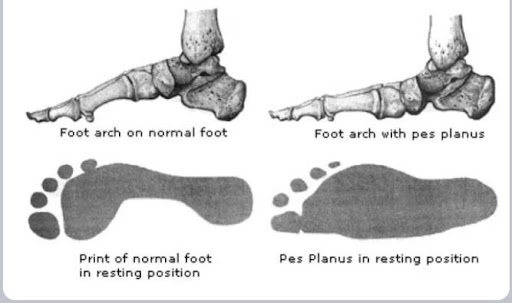
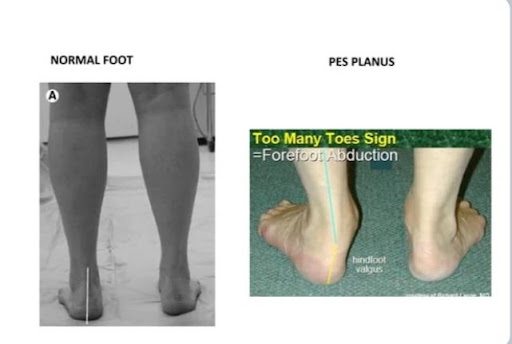
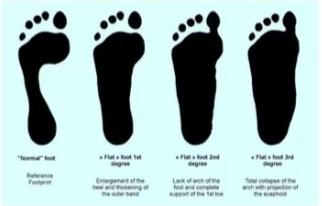
What is happening?
Talus is displaced from its normal position on hind foot or tarsal bones. It falls of its normal alignment with hind foot bones Talus turns inward and foot turns outward
- Talus sitting on top of hind foot bone
- Sinus tarsi is in open position
- Abnormal alignment
- Talus is not sitting on heel bone
- Partial collapse of sinus tarsi
- Partial talotarsal joint dislocation
- Excessive abnormal force acting on foot
Causes
Infants & children
- Heredity
- Laxity of ligaments
- Tight Achilles tendon
- Lack of foot exercise
Adults
Adults can develop flat feet through injury, tight Achilles tendon, abnormal joint formation, continued stresses on the foot and its arch, or simply as they age.Some of the most common causes of flat feet in adults are:
- Achilles Equinus contracture
- Coalition of rearfoot joints
- Failed or injured tendons
- Arthritis
- Marfan syndrome
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Overuse & strain
- Injury & fractures
- Age
Symptoms
- Inflammation of soft tissue
- Foot, arch, and leg fatigue
- Heel, foot, and ankle pain
- Knee, hip, and lower back pain
- Rolled-in ankles
- Abnormal walking patterns
- Shin splints
- Bunions
- Hammertoe
- Arthritis
- Plantar fasciitis
- Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD)
Pathomechanics of flat foot
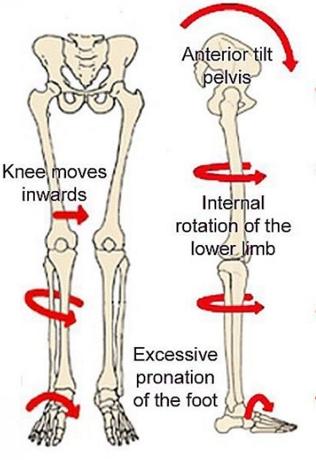
Kinetic chain
Pathology within a primary chain may be linked to dysfunction in a secondary chain, or vice versa.
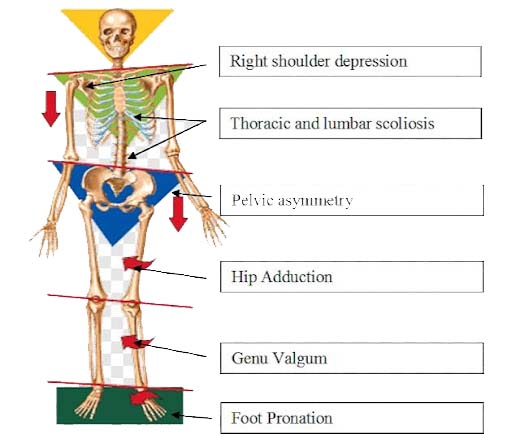
- Foot pronation causes tibial internal rotation, which causes knee valgus and hip internal rotation. During gait, the neuromuscular system must control these linked kinetic motions. Often, pathology is related to a dysfunction in compensation in the Kinetic chain: Through the kinetic chain, foot pronation may cause faulty lumbar positioning, requiring additional trunk stabilization.
- Based on kinetic chain system, flat foot deformity may resulted in patella lateral rotation and Q angle increasing that this agents fortunately resulted in knee pain.
- Weakness of the hip may lead to an inability to externally rotate the femur. This may in turn lead to an inability to achieve ideal resupination of the foot. Thus the screwhome mechanism (the coupled arthrokinematic relationship of extension and external rotation of the tibial plateau on the femur) needed for knee stability is compromised and patellofemoral pain may result
- Balance is maintained in the closed kinetic chain (the foot being fixed beneath the base of support) and relies on the integrated feedback and movement strategies among the hip, knee, and ankle, balance can be disrupted by diminished afferent feedback or deficiencies in the strength and mechanical stability of any joint or structure along the lower extremity kinetic chain.
- The lower extremity also plays a role in proprioceptive function. Afferent information from the foot is important for controlling posture and gait. The phenomenon of biped ambulation in humans is characterized by an intricate timing of biomechanical events presided over by subcortical programs and reflex reactions that can be modulated depending on the circumstances under which movement occurs.
- Abnormal walking patterns
- Foot malalignments that negatively affect foot mobility may diminish the ability of the lower leg to function optimally during weight-bearing stance
How Pregnancy Changes Your Lower Body
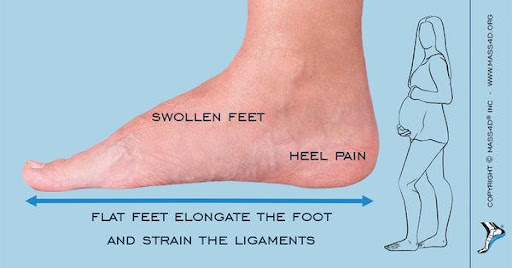
- Relaxin causes the ligaments all over the body to relax, including the feet
- The chances of getting soft tissue injury increase.
- The arch in your feet may flatten, which rolls your foot inwards while you stand or walk.
- Alignment in the lower body and back get disturbed, which commonly leads to foot problems, hip pain and back pain.
The weight gain, more significantly in the torso region.
|
He pelvis to tip forward and increase the lower back curve
|
Distribution of weight has changed in the torso region
|
It increases stress on the hips, legs, ankles, and feet.
|
This causes pain and swelling in the lower back, hips, legs, ankles, and the feet, and alters the posture as well as the gait
|
He pelvis to tip forward and increase the lower back curve
|
Distribution of weight has changed in the torso region
|
It increases stress on the hips, legs, ankles, and feet.
|
This causes pain and swelling in the lower back, hips, legs, ankles, and the feet, and alters the posture as well as the gait
Morphological variation of subtalar joint
- Morphological variations of the subtalar joint have subsequently been described by several authors, with the most striking variant being an absent anterior articulation . The anterior facet on the os calcis forms an integral part of the ‘acetabulum pedis’ supporting the talar head. Absence of this articulation could lead to a FF posture.
- Diagram showing the variation in the articulating surface morphology of the os calcis as described by Bruckner.14 A has three separate articular surfaces (anterior/middle/posterior). The anterior and middle articular surfaces joined in B and C. The anterior articular surface is missing in D.
- The hypothesis was that the morphology of the subtalar joint would be an important determinant of foot posture, in conjunction with the flexibility of the lower limb and BMI.
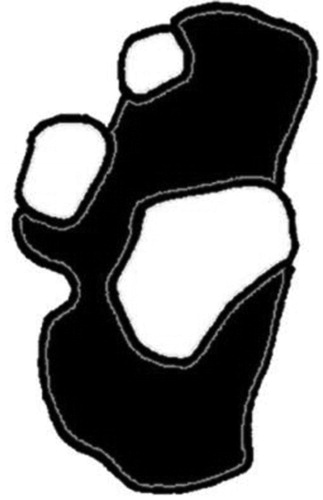
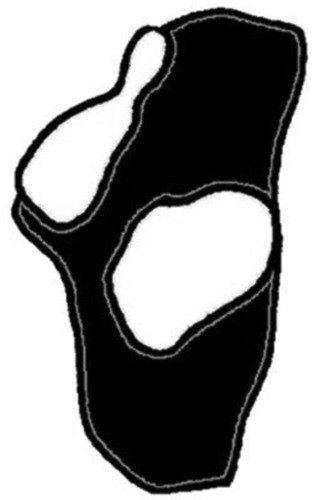


Clinical Assessment
- History - neonatal problem, family history
- Heel position
- Tiptoe test
- Jack's test
- Gait
- Sign of arthritis
- Spine, hip and knee
- ROM- ankle, subtalar, midtarsal joint
- Muscle tightness
- Muscle strength
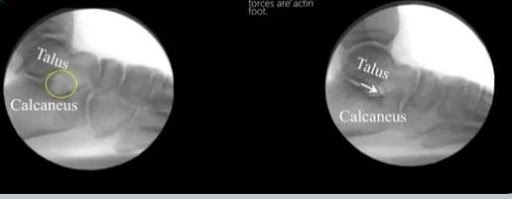
Radiological Features
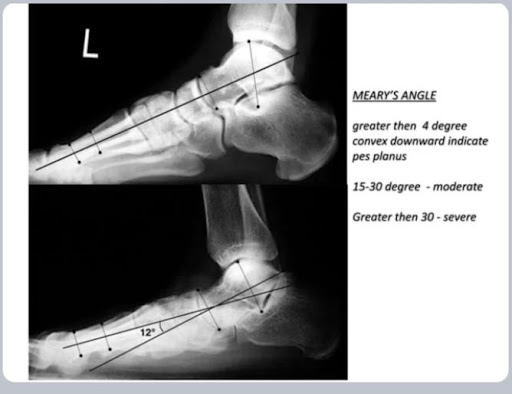
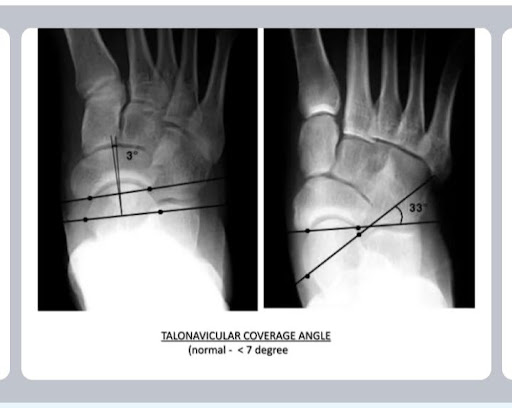
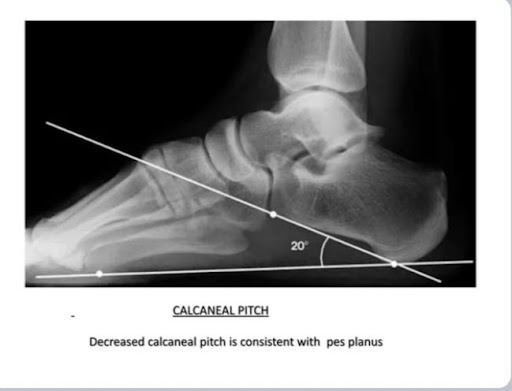
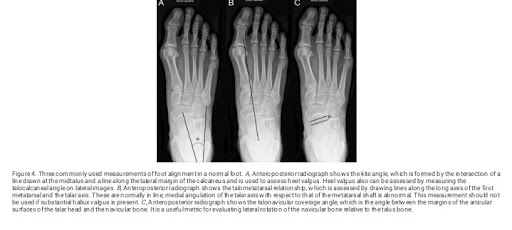
Physiotherapy Management
Modalities
- Heat and cold therapy-to enhance relaxation &reduces pain.
- Ultra sound and pulsed electrical stimulation -relieve the pain.
- Electric stimulation -to improve the blood circulation- healing process and reducing any swelling or discomfort.
- Strengthening exercises
- Stretching
- Posture correction exercises
- Orthotics
